Hello Rescuers!
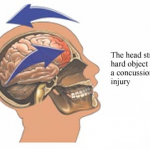
I received an email from a RoyOnRescue friend who had suffered a head injury while playing a sport. After being seen by the doctor he was diagnosed with Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis or (CVST). He had asked me if I would give my explanation of what it is and if it was something he should be worried about. His doctor had ex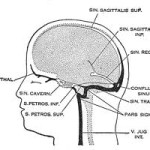 plained it but he was still a bit foggy regarding the diagnosis. Well, after looking into it from the clinical perspective, I realized that it was a pretty big deal and in some cases may be fatal. I researched multiple sources to gather credible information and when it all came down to brass tacks, I found that the Wikipedia explanation had done a pretty dog-gone good job of summarizing CSVT. So, with all credit given to them for most of this article and a link back to their website, here it is.
plained it but he was still a bit foggy regarding the diagnosis. Well, after looking into it from the clinical perspective, I realized that it was a pretty big deal and in some cases may be fatal. I researched multiple sources to gather credible information and when it all came down to brass tacks, I found that the Wikipedia explanation had done a pretty dog-gone good job of summarizing CSVT. So, with all credit given to them for most of this article and a link back to their website, here it is.
I have personally responded and treated many different types of head injuries as a paramedic but had not researched this problem to this level. Then, shortly after receiving this question, I read that Secretary of State, Hillary Clinton was diagnosed and hospitalized with the very same problem secondary to her head injury! Ironic. So, I thought to myself, if two people experienced this problem secondary to a common traumatic head injury(concussion), there may be more with the same question.
Here’s my trimmed-down version of what it is, what it’s symptoms are, how to determine if it is truly CSVT and then what a person may want to do if they think they may be suffering from such a complication. So let’s dig into some of the questions you may have! P.S. You’ll notice there are more links then usual in this article. The topic is so complex and has so many different facets I thought it wise to allow you to do some of your own information mining and hope the links make it easier.
Q: What is a cerebral venous sinus thrombosis anyway?
A: A CVST is the presence of thrombosis (a blood clot) in the dural venous sinuses, which drain blood from the brain.
Q: What causes a CVST?
A: There can be many causes of CVST. Here is a few I included:
- Thrombophilia, a tendency to develop blood clots due to abnormalities in coagulation, e.g. factor V Leiden, deficiency of protein C, protein S or antithrombin, or related problems
- Nephrotic syndrome, a kidney problem causing protein loss in the urine
- Chronic inflammatory diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, lupus and Behçet’s disease
- Pregnancy and puerperium (the period after giving birth)
- Particular blood disorders, especially polycythemia vera and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
- Use of estrogen-containing forms of hormonal contraception
- Meningitis and infections of the ear, nose and throat area such as mastoiditis and sinusitis
- Direct injury to the venous sinuses
- Medical procedures in the head and neck area
- Sickle cell anemia
- Dehydration, primarily in infants and children
- Homocystinuria
Q: How might I know if I have a CVST?
A: Headache that may worsen over the period of several days, but may also develop suddenly. Strangely the headache may be the only symptom of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Stroke, 40% of all patients have seizures, Common symptoms in the elderly with this condition are otherwise unexplained changes in mental status and a depressed level of consciousness. The pressure around the brain may rise, causing papilledema (swelling of the optic disc) which may be experienced as visual problems. In severely raised intracranial pressure, the level of consciousness is decreased, the blood pressure rises, the heart rate falls. This is a common symptom found in closed head injuries which makes sense as the mechanism is very similar.
Q: How will the doctor know if this is what I have?
A: The most commonly used tests are computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), both using various types of radiocontrast to perform a venogram and visualise the veins around the brain
Q: How is a CVST treated and cured?
A: Treatment is with anticoagulants (medication that suppresses blood clotting), and rarely thrombolysis (enzymatic destruction of the blood clot). Given that there is usually an underlying cause for the disease, tests may be performed to look for these. The disease may be complicated by raised intracranial pressure, which may warrant surgical intervention such as the placement of a shunt.
A: Yes. Like any illness or injury that causes a problem with the circulation of oxygenated blood to our tissues, this type of problem can be very dangerous if left untreated. It also runs a risk of complication in that it raises the intracranial pressures which can act similar to a closed head injury and this too can cause severe injury or death. If a person has any of the symptoms listed above, they should be seen as soon as possible to rule out this potentially life threatening disorder. If a person is reacting with decreased level of consciousness, or any type of life threatening complications, activation of Emergency Medical Services or 911 should be immediate with life saving or time buying intervention given.
I hope this helps and keep well!
See Source:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cerebral_venous_sinus_thrombosis
http://neurology.jwatch.org/cgi/content/full/2007/515/2
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/705510_3